Initialize contract
Overview
In this course, we will use Remix to run the Solidity contract.
Remix is the official recommended integrated development environment (IDE) for smart contracts on Ethereum. It is suitable for novices. It provides an easy-to-use interface to quickly write, compile and deploy smart contracts in the browser without installing any programs locally.
Solidity is a high-level programming language created for implementing smart contracts. This language is influenced by the C++, Python and JavaScript languages, and is designed to run on the Ethereum virtual machine (EVM). Solidity is a statically typed language that supports inheritance, libraries, and complex user-defined types.
Panel
Enter Remix, we can see the interface as shown in the figure below:
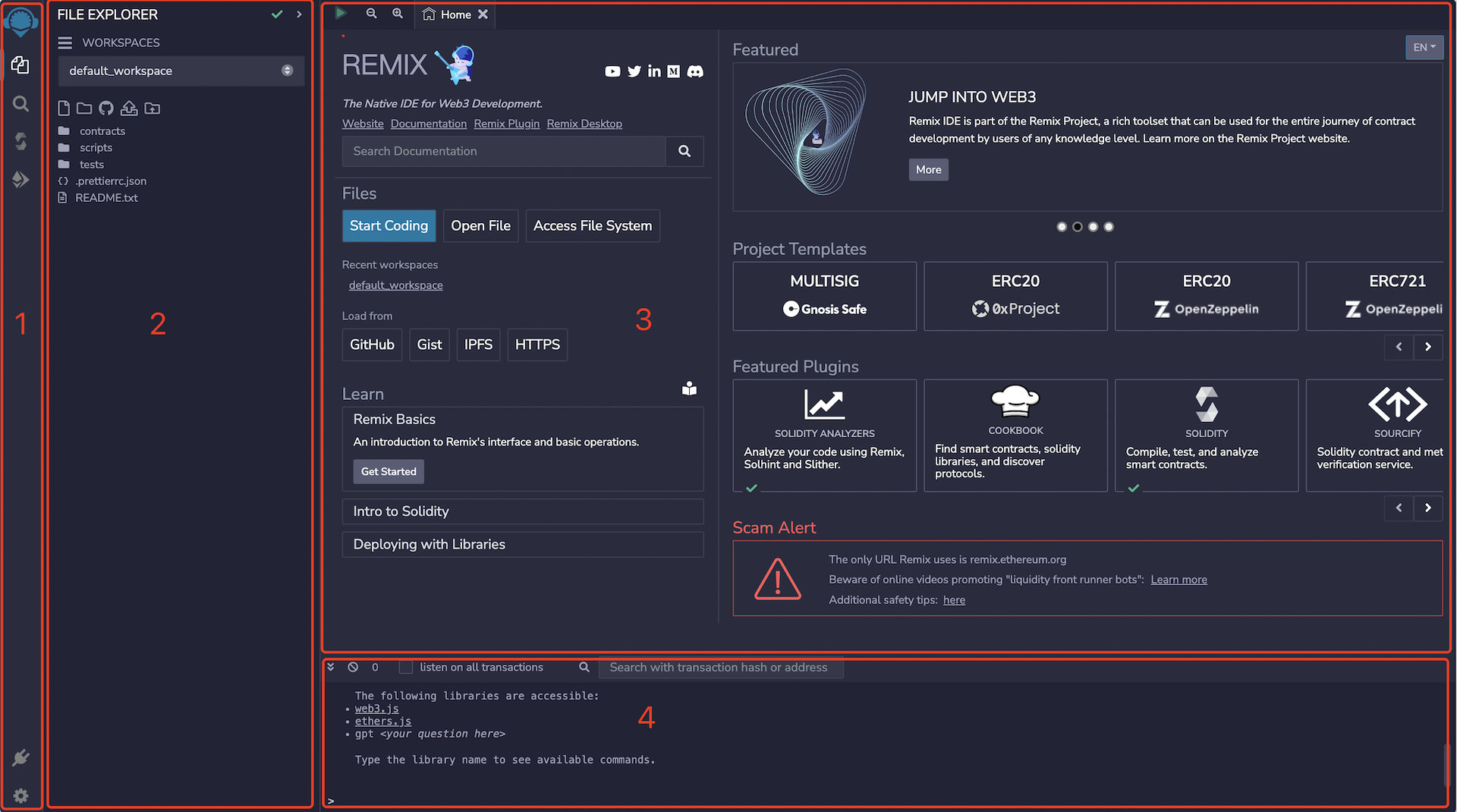
As you can see, Remix consists of three panels and a terminal.
- Icon panel-click to change the plug-in displayed in the side panel;
- Side panel-most of the interfaces of the plug-in (not all plug-ins) are here;
- Main panel-used to edit files, large-scale tools and home page tabs;
- Terminal-for viewing transaction receipts and various logs.
Icon panel

A brief introduction to the side panel icon function, we will have a more detailed introduction when we use it later. Home can always open the main page, even if it is turned off. File explorer is used to manage workspaces and files. Search is a global search function. Solidity Compiler is the interface of the contract compiler. The interface displays the basic configuration items of the compiler by default, and the Advanced Configurations button opens the advanced configuration panel. Deploy&Run is to send the transaction to the current environment. Debugger is a debugger. When debugging a transaction, the debugger will display the status of the contract. Plugin Manager is a plug-in manager, there are many plug-ins to choose from. Setting will have some basic settings, such as language, theme, GitHub access token, general settings, etc.
Workspace and file
The WORKSPACES in Remix is a special folder that separates projects. The files in a workspace cannot import or access files in another workspace. As shown in the figure below, click icon 1 to switch different workspaces, and icon 2 can perform a series of operations on the workspace, such as Create, Clone, Rename, Download, Delete, etc.
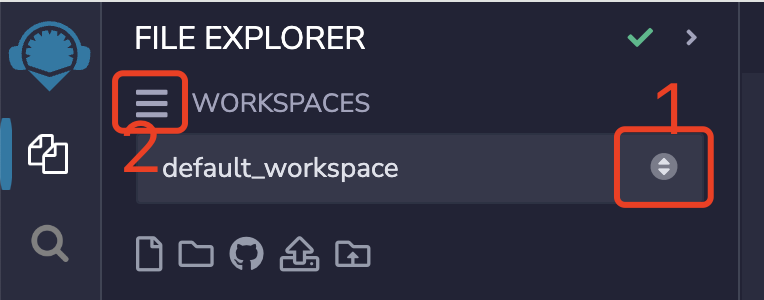
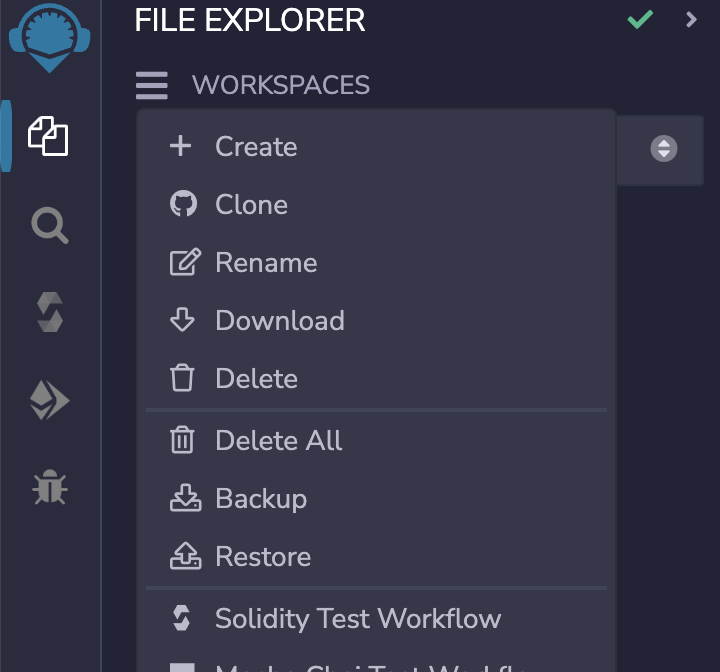
Create
We will demonstrate through the Create button in this tutorial. When we click Create, the Create Workspace pop-up window will pop up. Remix provides the following templates:
- Basic
- Blank
- OpenZeppelin ERC20
- OpenZeppelin ERC721
- OpenZeppelin ERC1155
- 0xProject ERC20
- Gnosis Safe
When you select an ERC721 template of the OpenZeppelin library, you can add additional features.
ERC721 (Ethereum Request for Comments 721), proposed by William Entriken, Dieter Shirley, Jacob Evans, Nastasia Sachs in January 2018, is a non-homogeneous token standard that implements token APIs in smart contracts. OpenZeppelin is a library for secure smart contract development, which contains the standard implementation of many commonly used contracts.
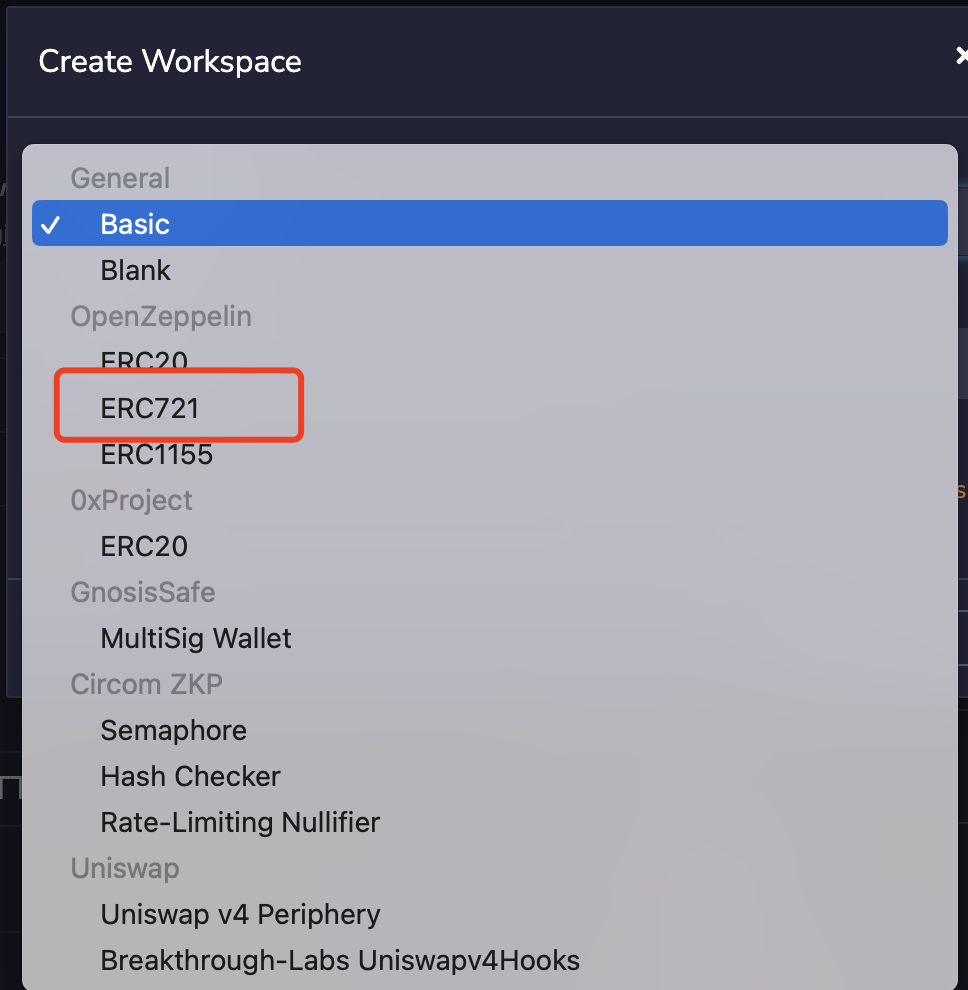
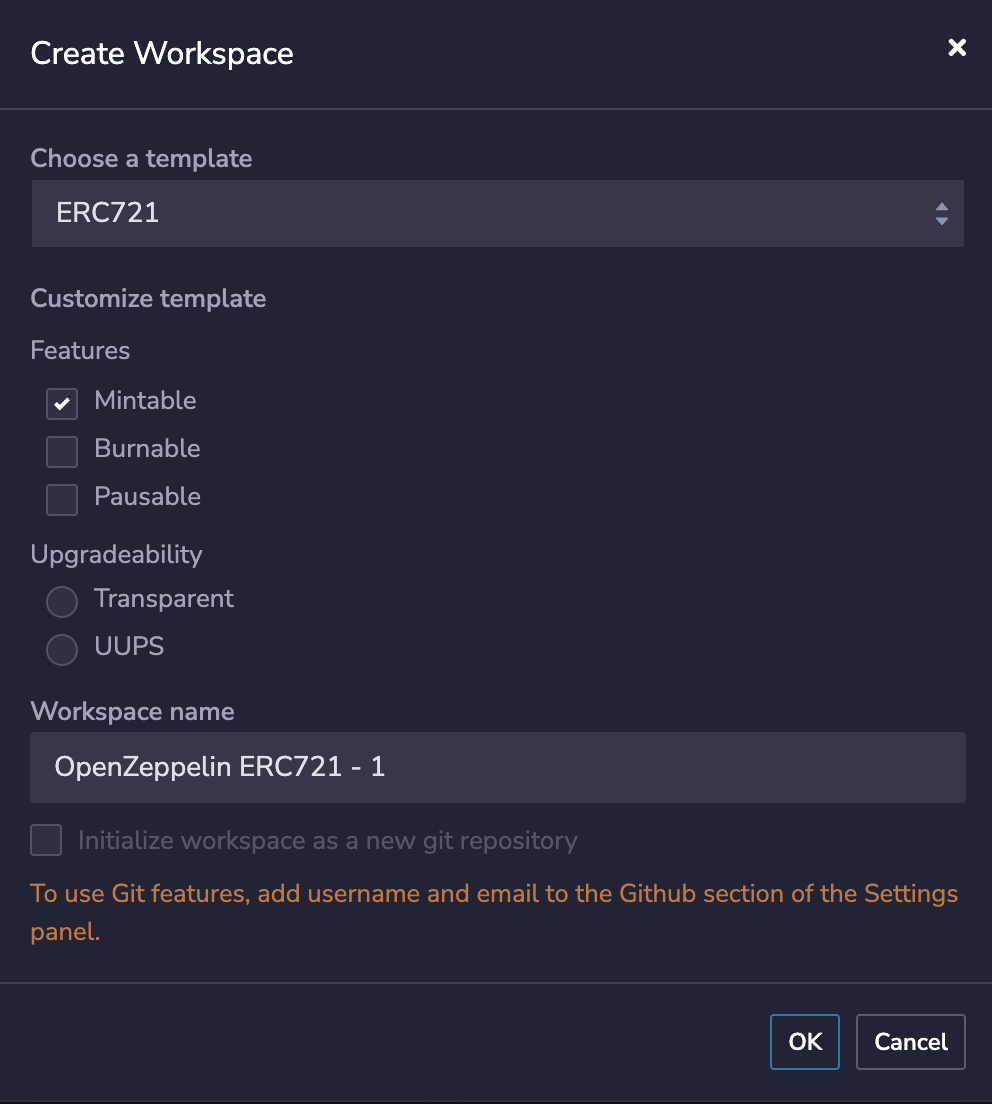
Check Mintable, which means that we add the Mint method to the template contract, and then click OK. Here, our Workspace is created. As shown in the figure below:
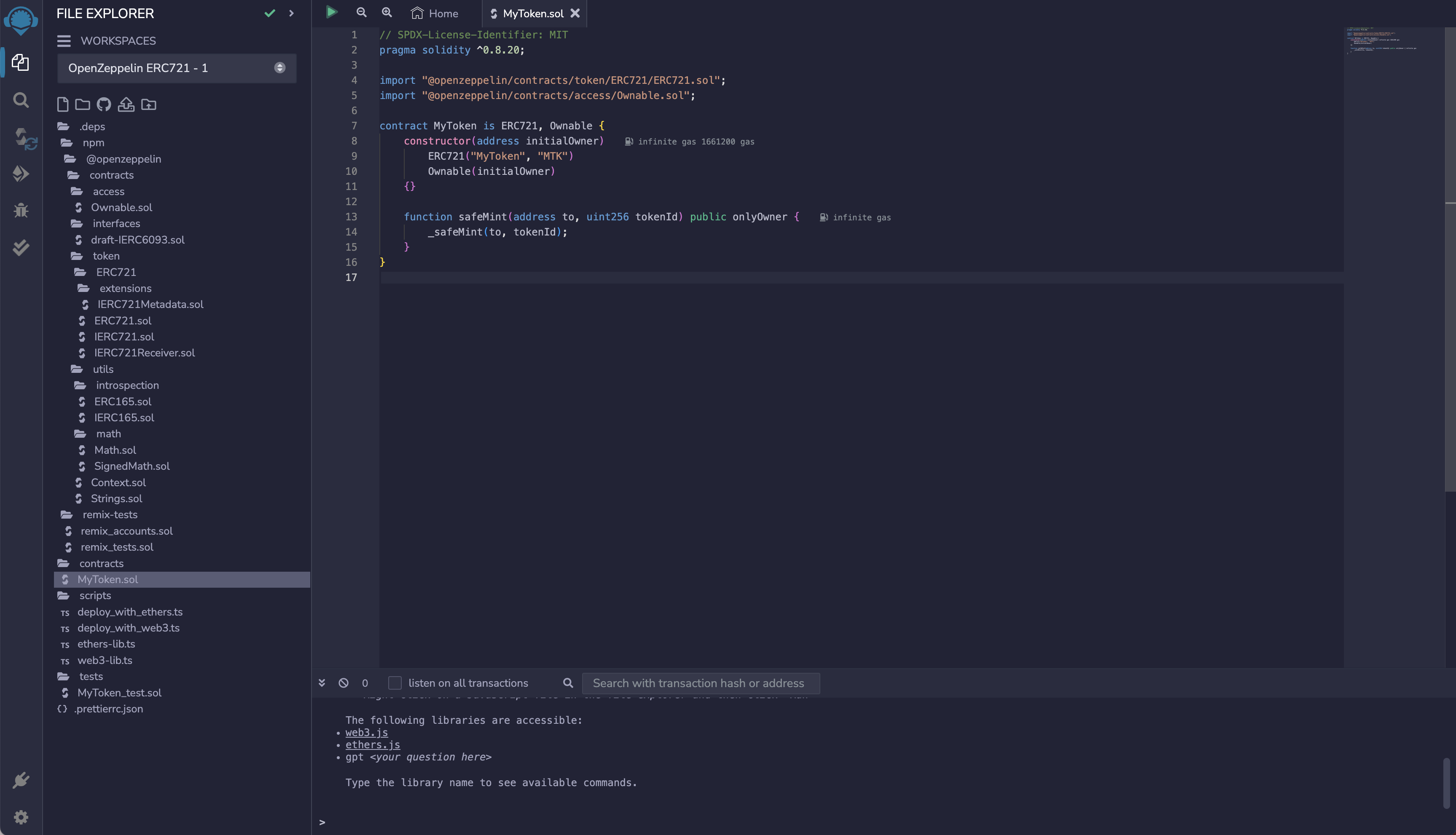
.deps directory contains the npm package of @openzeppelin we installed. The contract template referenced in our contract is installed here, as well as the toolkit referenced in the contract template. contracts is the contract file written by ourselves. scripts folder contains the automatically generated script files for deploying contracts. You can also deploy contracts by executing the js file below this. tests automatically writes some automatic verification test files.
@openzeppelin provides us with the ERC721 contract template in contracts/MyToken.sol, let's take a brief look at the content of this contract.
- The first line is a comment, which will write the software license (
license) used by this code. Here we useMIT license. If no license is written, a warning (warning) will be issued during compilation, but the program can run.soliditycomments start with//, followed by the content of the comment (will not be executed by the program). - The second line declares the
solidityversion used by the source file, because different versions have different syntax. This line of code means that the source file will not allow compilers less than version0.8.20or greater than or equal to0.9.0to compile (the second condition is provided by^).Soliditystatements end with a semicolon (;). - The 4-5 lines import external
Solidityfiles, and the importedSolidityfiles and theSolidityfiles themselves are equivalent to the sameSoliditycontract. - Line 7 creates a contract (
contract) and declares the name of the contract asMyToken. The keywordisindicates that the contract inherits the importedERC721andOwnablecontracts. - Lines 8-10, within the
constructor, we pass the predefined parameters of the inherited contracts. ForERC721, we pass thenameandsymbolof thetoken, and forOwnable, we pass the address of the contract owner. - Lines 13-15 define a
publicmethod calledsafeMint, which is accessible to the outside world. This method requires two parameters:to, of typeaddress, andtokenId, of typeuint256. Inside the method, the private method_safeMint()from theERC721.solcontract is executed, along with the providedtoandtokenIdparameters.
Next, we will try to write some custom functions to the contract template.
